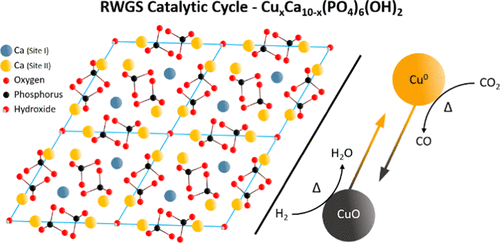
In this work, Guo et al. use abundant and nontoxic hydroxyapatite to demonstrate high activity at a low cost by replacing constituent cations with transition metals to also enable tailoring of its catalytic properties. Using this method, the facile and scalable synthesis of a copper-substituted hydroxyapatite catalyst is presented, demonstrating its high activity in the reverse water gas shift reaction. Thorough in situ characterization using X-ray absorption and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic methods provides unrivalled insight into both the structure of the active catalyst and the speciation of reaction intermediates. It is thus shown that this copper-substituted hydroxyapatite catalyst is an exemplary candidate for use in large-scale carbon dioxide reduction systems. See full article at ACS Catalysis.
